View source or report issues on GitHub
All Algorithms We have Traced This year
As we trace and construct new algorithms in class, I will add them to this page as reference, with solutions.
When you are constructing an algorithm in pseudocode, it may help to use this pseudocode simulator made by IB CS teacher Dave Mulkey. It allows you to actually run pseudocode and see if it works!
Unit 1
First algorithm ever!
This was done on August 6 in HL, August 7 in SL
Algorithm
Solution
Click to expand answer
K: 47 37 26 14
N: 10 11 12 13
D: 37 26 14 1
Output: 47 37 26 14
Algorithm 2
This was done on August 8 in HL, August 9 in SL
Algorithm
Solution
Click to expand answer
Run 1
T: 42 31 20 9
F: 11
Output: 9
Run 2
T: 19 9
F: 10
Output: 9
Run 3
T: 25 20 15 10 5 0
F: 5
Output: 0
The output is the REMAINDER when T is divided by F.
Algorithm 3
This was done on August 12 in HL, August 13 in SL. This comes directly from the May 2018 SL Paper.
Prior Knowledge Needed
You need to know that A mod B means “The remainder when A is divided by B”. So the value of 11 mod 3 is 2, because 11/3 is 3 with a remainder of 2.
You also need to know that A div B means to do division but drop the decimal part (not round, just ignore it!) So the value of 11 div 3 is 3.
Algorithm
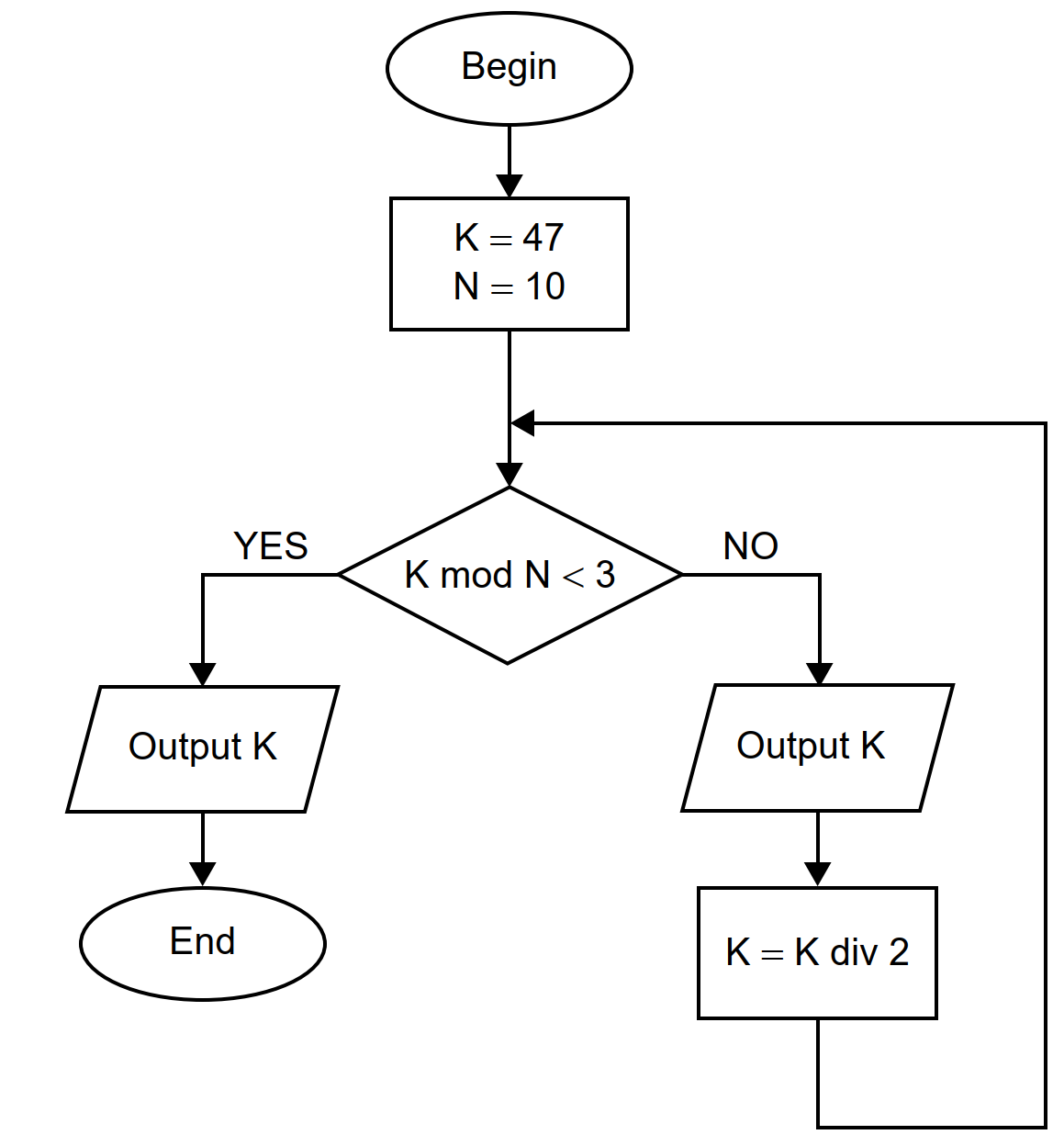
Solution
Click to expand answer
K: 47 23 11
N: 10 10 10
Output: 47 23 11
Algorithm 4
Trace for N = 6 and N = 7
Algorithm
SUM = 0
loop COUNT from 1 to (N div 2)
if N mod COUNT = 0 then
SUM = SUM + COUNT
end if
end loop
if SUM = N then
output "perfect"
else
output "not perfect"
end if
Solution
Click to expand answer
SUM: 0 1 3 6
COUNT: 1 2 3
N: 6
Output: "perfect"
SUM: 0 1 1 1
COUNT: 1 2 3
N: 7
Output: "not perfect"
Algorithm 4
Introducing arrays!
Algorithm
Trace the algorithm below for STOCKS = [42, 11, 6, 3]
COUNT = 0
TOTAL = 0
loop N from 0 to STOCKS.length - 1
if STOCKS[N] ≠ 0 then
COUNT = COUNT + 1
TOTAL = TOTAL + STOCK[N]
end if
end loop
if COUNT ≠ 0 then
AVERAGE = TOTAL / COUNT
output "Average = ", AVERAGE
else
output "There are no non-zero values"
end if
Solution
Click to expand answer
STOCKS = [42, 11, 6, 3]
N: 0 1 2 3
COUNT: 1 2 3 4
TOTAL: 0 42 53 59 62
AVERAGE: 15.5
output: "Average = 15.5"
Algorithm 5
Construct code that would accept an array of strings named FIRST and an array of strings named LAST (you can assume they are the same length) and loop through both of them, outputting the joined names in LAST, FIRST format.
Some possible solutions
Pseudocode
Click to expand answer
1
2
3
loop N from 0 to FIRST.length - 1
output LAST[N], ", ", FIRST[N]
end loop
Typescript
1
2
3
for (let i = 0; i < FIRST.length; i++) {
output(LAST[i] + ", " + FIRST[i]);
}
Algorithm 6
Collections!
Algorithm
Trace the algorithm below for a collection NAMES with the values {David, Jake, Ross, David, Jim}
// Assume LIST is an array with plenty of room, but currently empty
COUNT = 0 // number of names currently added to array LIST
loop while NAMES.hasNext()
DATA = NAMES.getNext()
FOUND = false
loop POS from 0 to COUNT - 1
if DATA = LIST[POS] then
FOUND = TRUE
end if
end loop
if FOUND = false then
LIST[COUNT] = DATA
COUNT = COUNT + 1
end if
end loop
output LIST
Solution
Click to expand answer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
LIST: [] [David] [David, Jake] [David,Jake,Ross] //same [David,Jake,Ross,Jim]
COUNT: 0 1 2 3 //same
DATA: David Jake Ross David Jim
FOUND: f f f f f t t t f f f f f
POS: 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 1 2 3
output: [David, Jake, Ross, Jim]
This algorithm moves items from a list to an array, ignoring duplicate values
Algorithm 7
Imagine you have an array called SCORES that represents all the scores a player has earned on a video game (all positive numbers). The array is NOT sorted. Construct an algorithm that finds the highest score and outputs the sentence “Your high score is: __” (with the correct high score in the blank). NOTE: You should NOT initialize SCORES in your algorithm - you should assume it exists before your algorithm starts.
Solution
Click to expand answer
HIGH=0
loop i from 0 to SCORES.length
if SCORES[i]>HIGH then
HIGH=SCORES[i]
end if
end loop
output "Your high score is " + HIGH
# to test your own code, add the line SCORES = [1, 44, 2, 4] above your algorithm
# in the simulator linked at top, and look for output "Your high score is 44".
Algorithm 8
Construct an algorithm identical to the one for algorithm 7, but using an IB Collection called SCORES rather than an array.
Solution
Click to expand answer
SCORES.resetNext()
HIGH = 0
loop while SCORES.hasNext()
A = SCORES.getNext()
if A > HIGH then
HIGH = A
end if
end loop
output "Your high score is " + HIGH
# To test your own code, add the lines below before your algorithm in the simulator:
# SCORES = new Collection()
# SCORES.addItem(1)
# SCORES.addItem(44)
# SCORES.addItem(3)
# If your code runs correctly, the output will be "Your high score is 44".
Algorithm 9
Predict the output of the code below. The firstLetter function returns the first letter of a string.
Algorithm
NAMES = new Collection()
NAMES.addItem("Bob")
NAMES.addItem("Dave")
NAMES.addItem("Betty")
NAMES.addItem("Kim")
NAMES.addItem("Debbie")
NAMES.addItem("Lucy")
NAMES.resetNext()
loop while NAMES.hasNext()
NAME = NAMES.getNext()
if firstLetter(NAME) = "D" then
output NAME
end if
end loop
Solution
Click to expand answer
1
2
Dave
Debbie
Algorithm 10
Imagine you have an IB collection called NAMES. Construct an algorithm that will take the collection and output a single sentence in the form The names are: {Bob Mary Joe Dave }
Solution
Click to expand answer
OUT = "The names are: {"
NAMES.resetNext()
loop while NAMES.hasNext()
OUT = OUT + NAMES.getNext() + " "
end loop
OUT = OUT + "}"
output OUT
# You can check your answer by copying the NAMES setup information from Algorithm 9
# into the pseudocode simulator then adding your algorithm underneath
# but remember, if your pseudocode isn't perfect you can still get full credit
Algorithm 11
This one comes from FIS’s list of old algorithms
The following algorithm fragment has been designed to analyse the temperatures at a tourist resort.
COUNT = 0
TOTAL = 0
TEMP = input("Enter a temperature")
BIG = TEMP
loop while not(TEMP = 0)
TOTAL = TOTAL + TEMP
COUNT = COUNT + 1
input TEMP
if TEMP > BIG then
BIG = TEMP
endif
end loop
AVERAGE = TOTAL / COUNT
output AVERAGE, BIG
Copy, add lines, and complete the trace table below, assuming the user enters the data 15, 7, 23, 9, 0
| Count | Total | Temp | Big | not (TEMP = 0) | output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 15 | |||
Algorithm 12
Consider the fragment of code below:
X = 1
loop while X < 6
Y = 1
loop while Y < 5
Y = Y + 1
end loop
output “The product of X and Y is ”, X * Y
output “The values of X and Y are ”, X, Y
X = X + 1
end loop
Write down the complete output of this algorithm (no full trace required)
Algorithm 13
Consider the fragment of code below:
X = 1
loop while X < 6
Y = 1
loop while Y < 6
output “The product of X and Y is ”, X * Y
Y <-- Y + 2
end loop
output “The values of X and Y are ”, X, Y
X = X + 2
end loop
Write down the complete output of this algorithm (no full trace required)